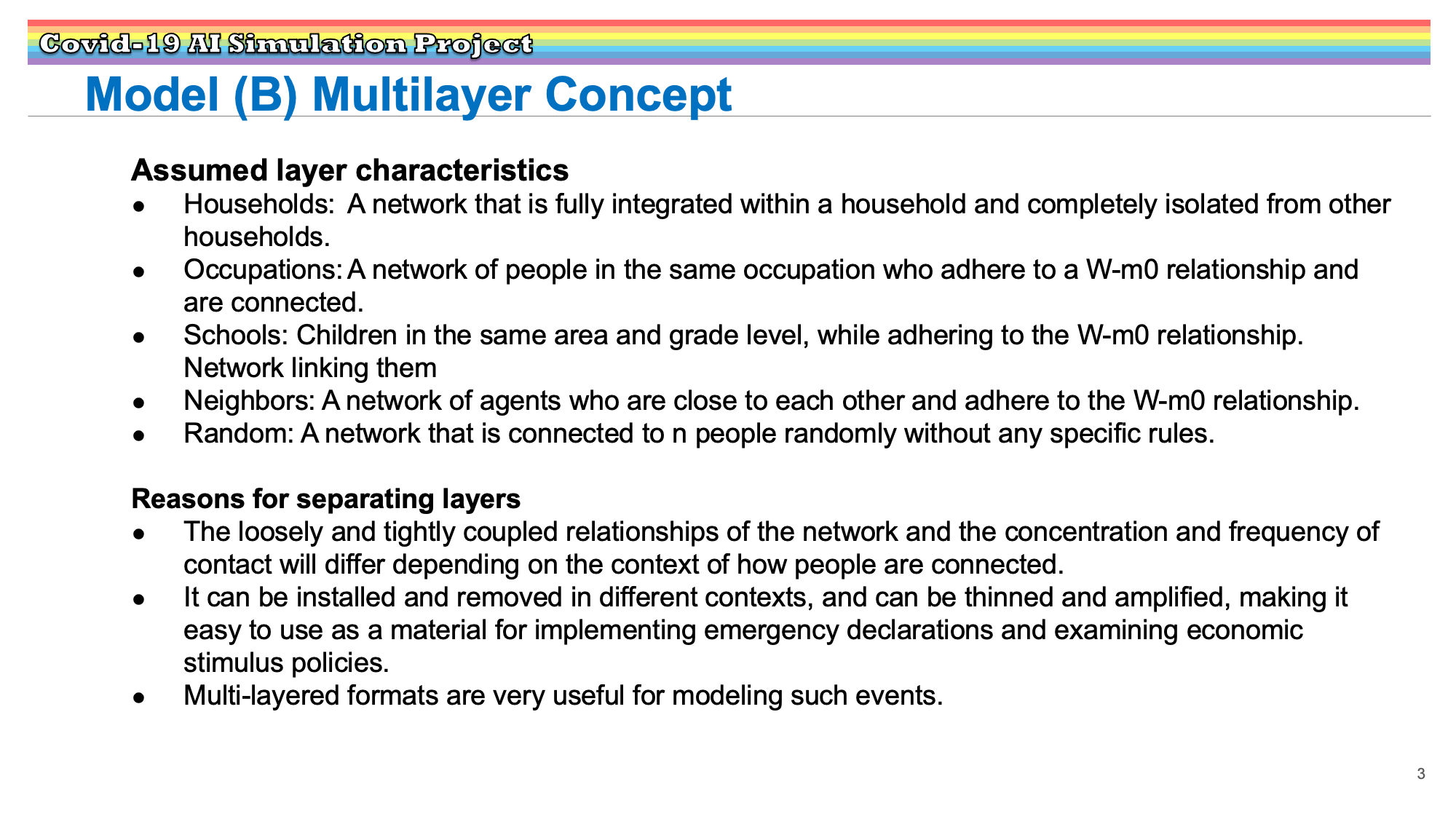
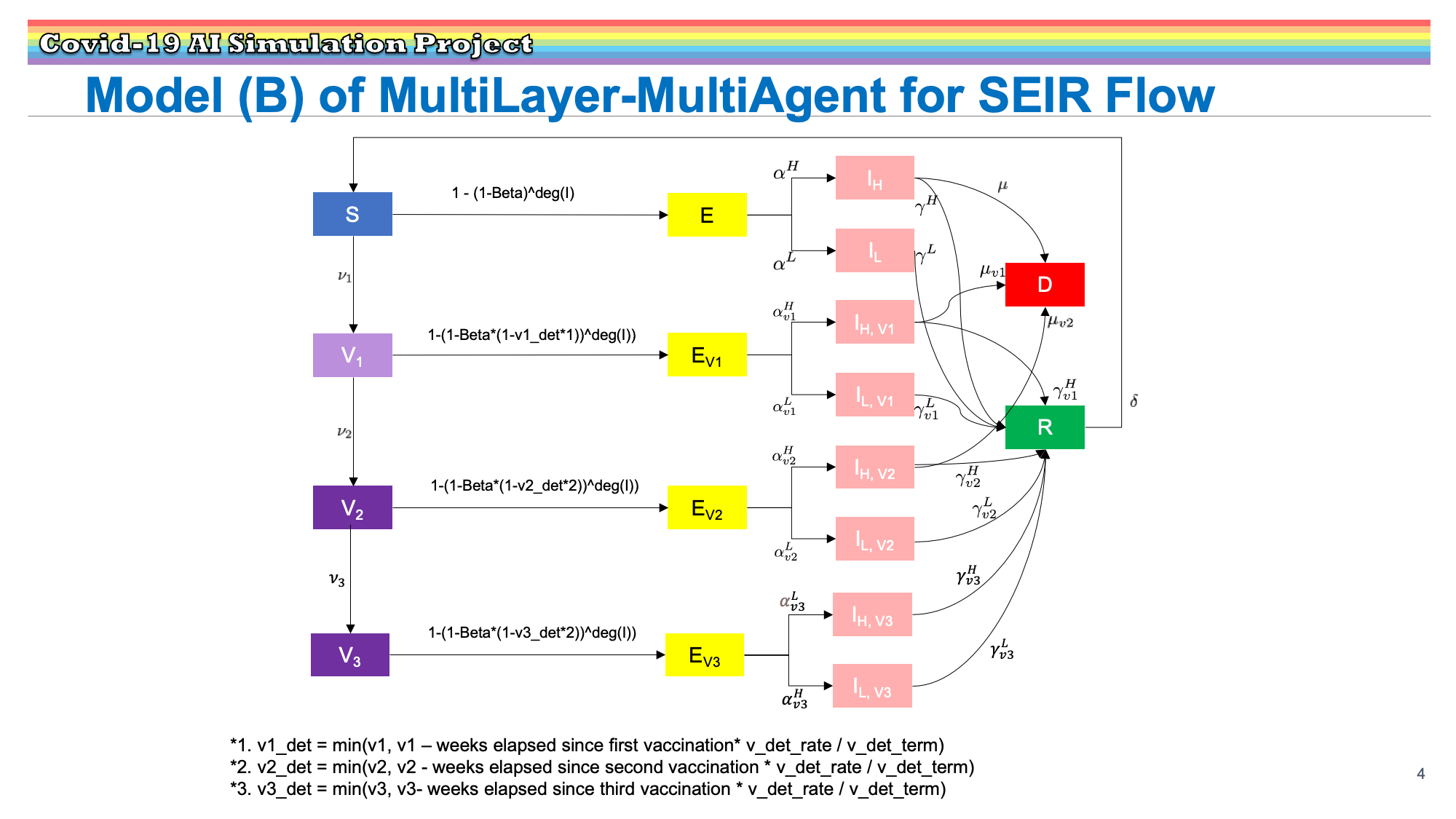
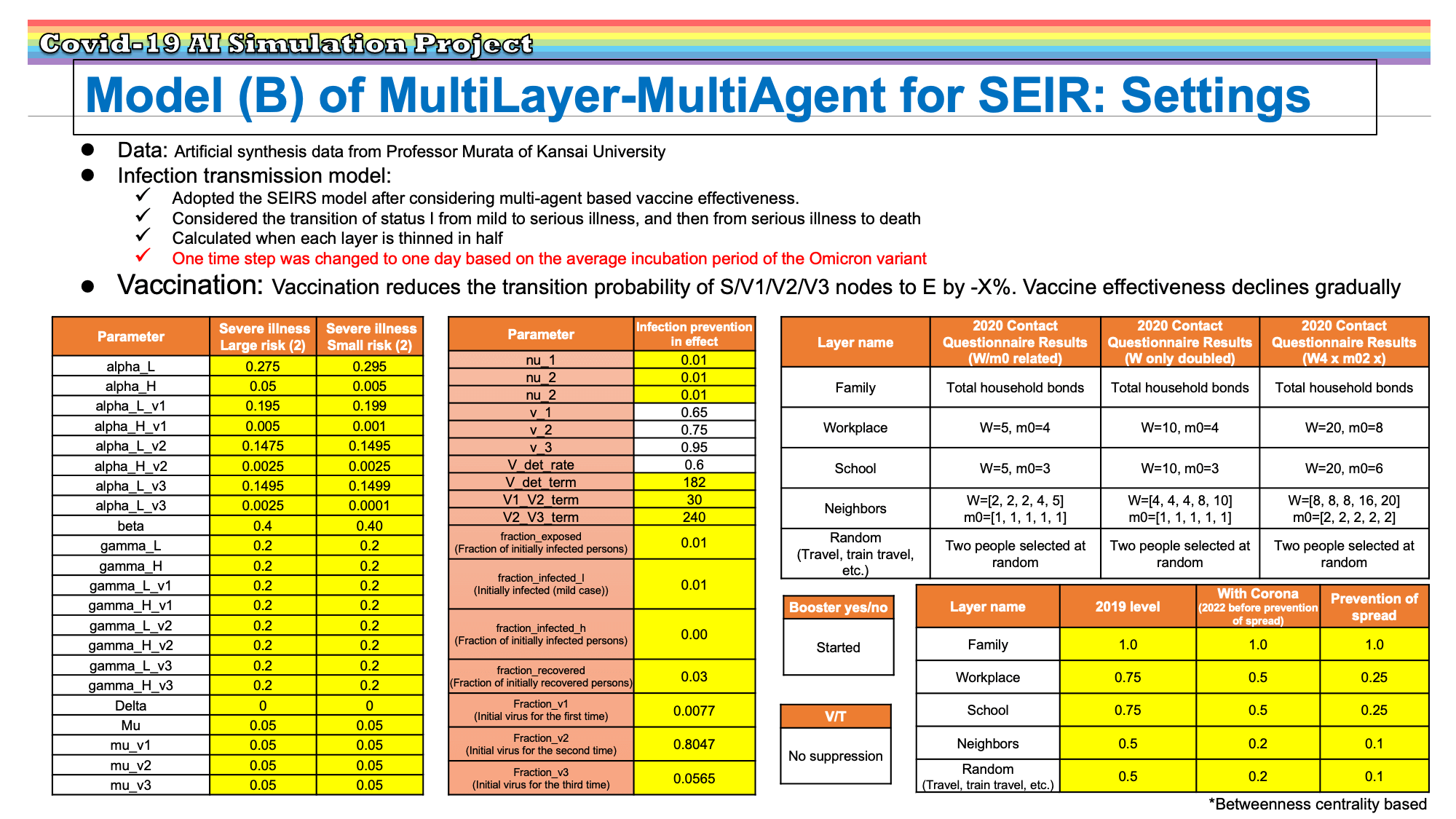
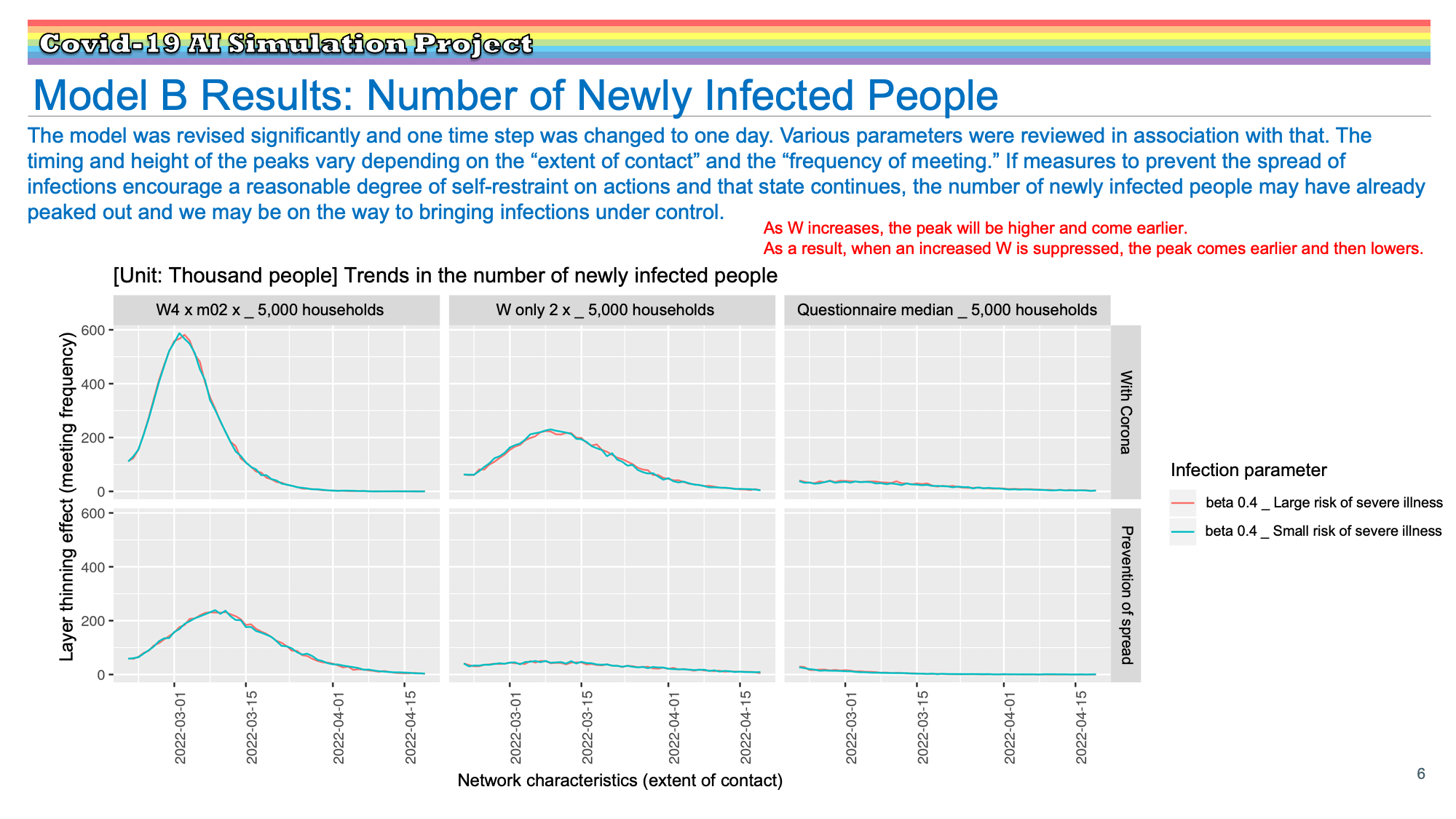
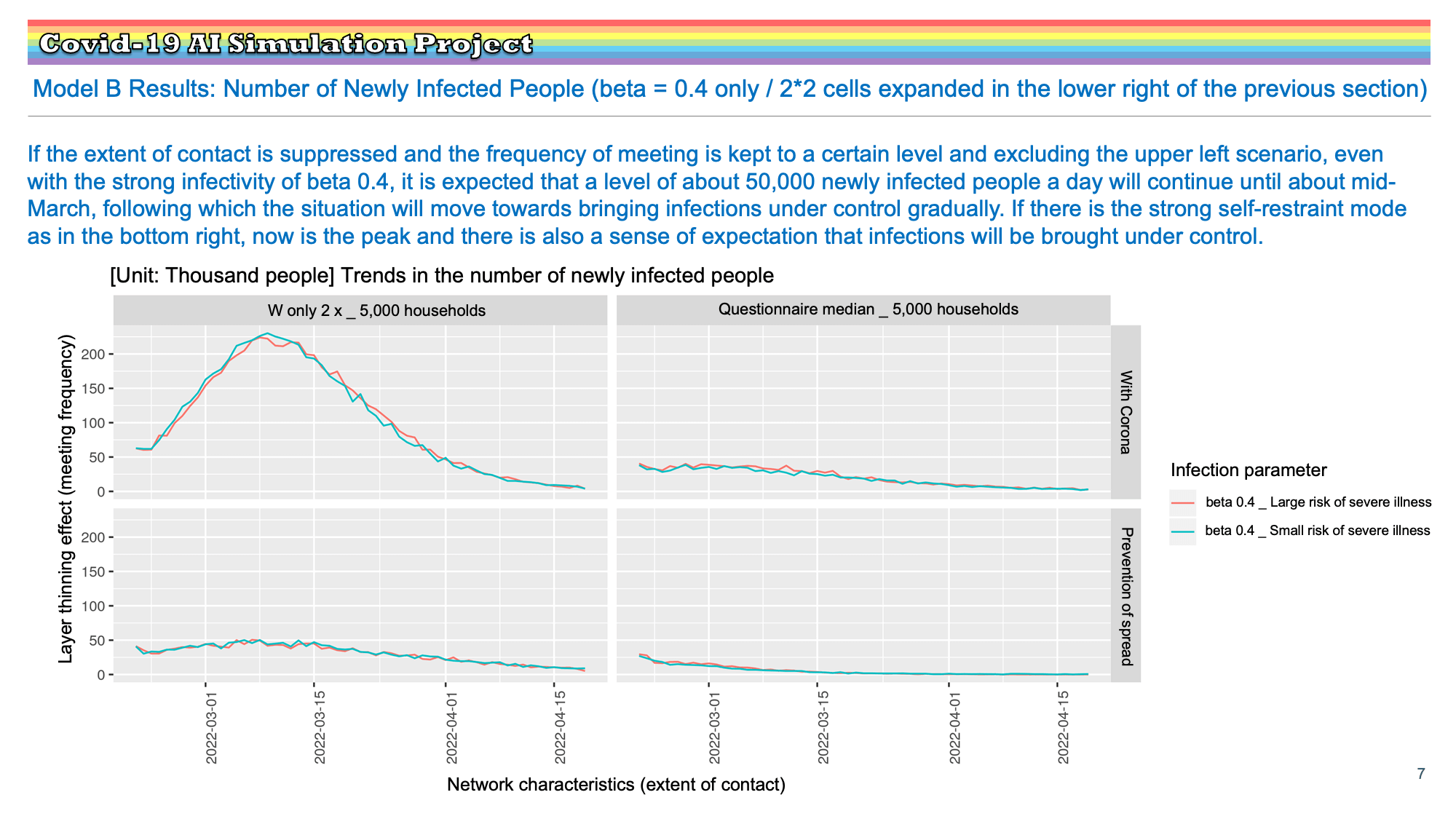
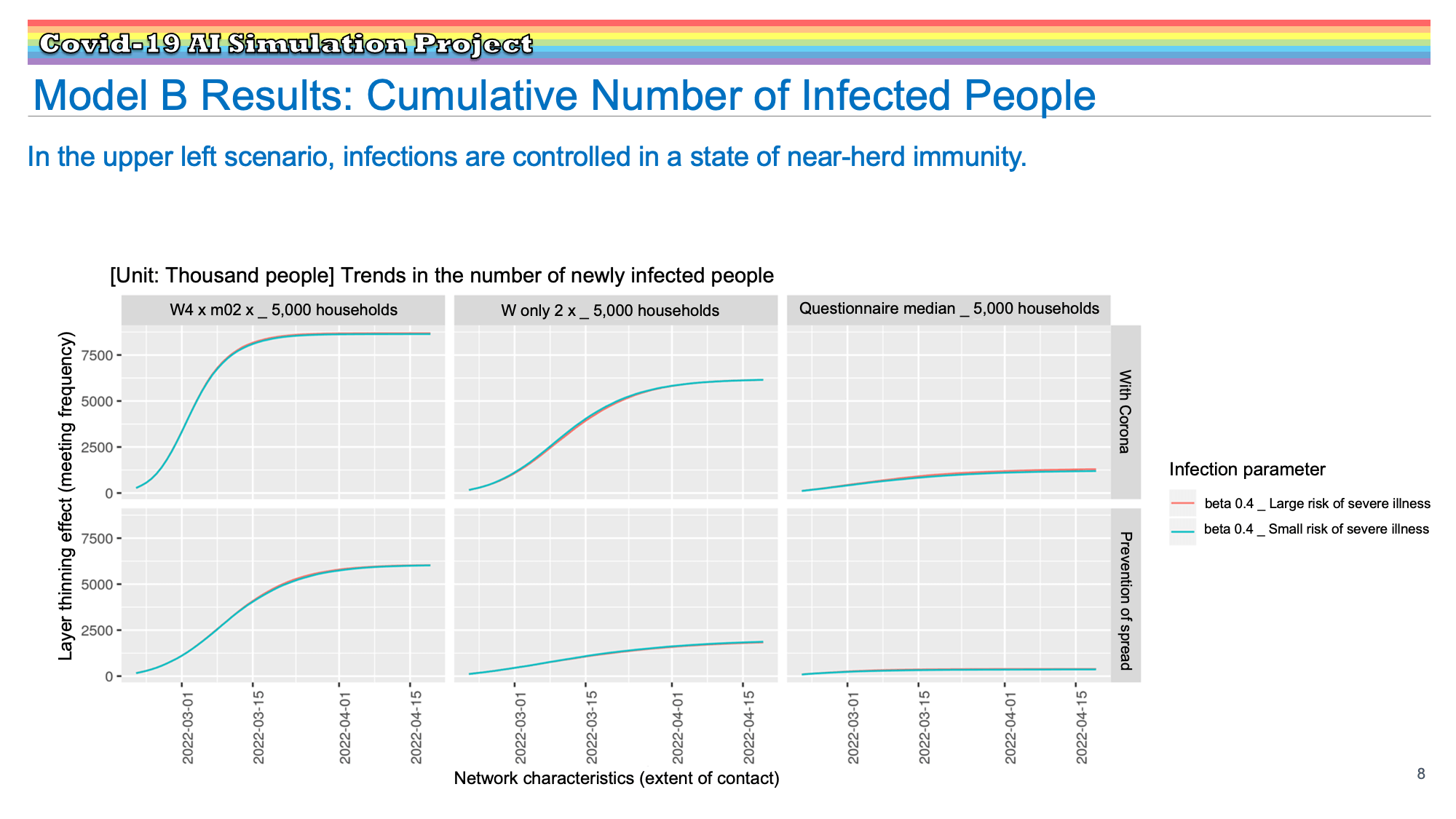
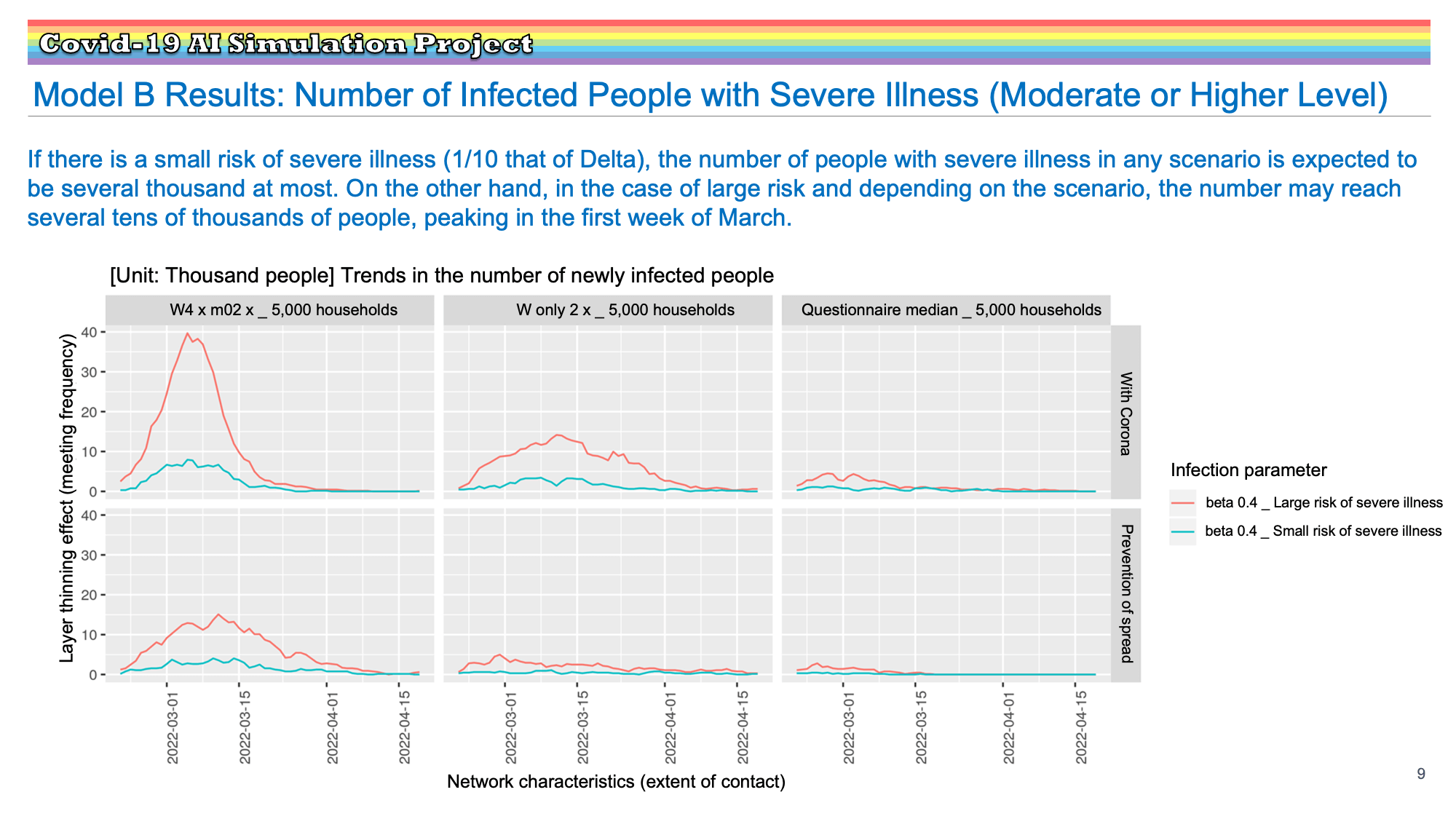
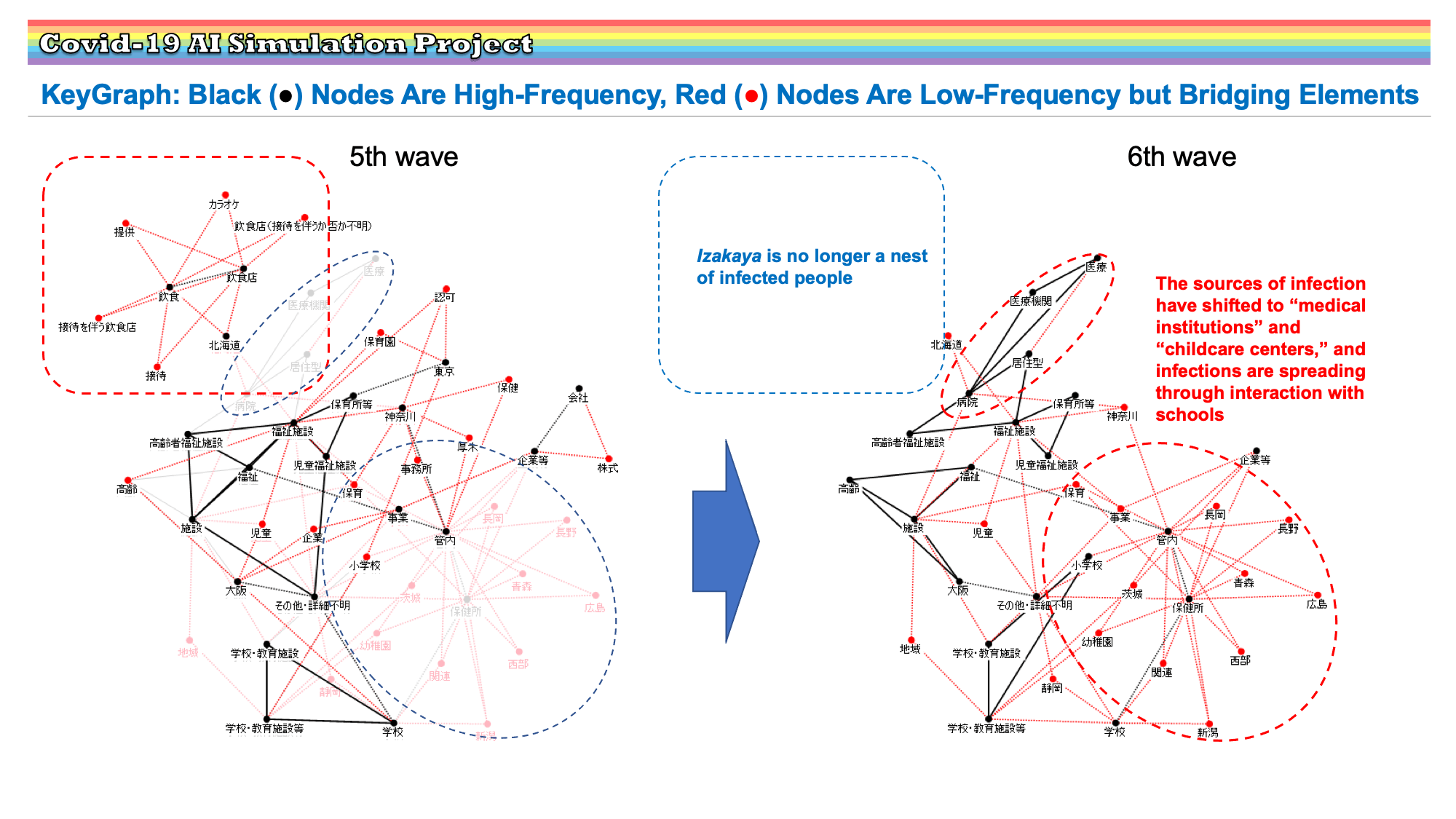
Research Results:RQ3_2021
Simulation of infection spread and control
Related reports

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa
No need to be afraid of infection numbers – In the case of the low severity rate scenario #4
2022.03.08
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Divorce rates during COVID-19
2022.03.08
Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Marriage and birth rates during COVID-19
2022.03.01
Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Estimates of the number of daycare closures
2022.02.15
Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Birth rates during COVID-19
2022.02.08
Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Marriage rates during COVID-19
2022.02.08
Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Outlook for COVID-19 and Economic Activity – Impact of stricter hospitalization standards #9
2022.01.25
Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

No need to be afraid of infection numbers – Towards post-corona era (low severity scenario)
2022.01.25
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Projection of the number of new positive persons assuming the prevalence of Omicron variant
2021.12.21
Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Projection of the number of new positive persons assuming the prevalence of Omicron variant
2021.12.14
Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Five Reasons for the Decrease in the Number of Infected Persons and Findings for the Future
2021.12.14
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Booster Vaccination planning
2021.11.30
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Impact of active domestic travels
2021.11.16
Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Revised plan of the new Shimoda Model
2021.11.16
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Wave Flow in KeyGraph: waves are not over
2021.10.26
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Strategy Cocktail
2021.10.05
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa
Effect of Antibody Cocktail
2021.10.05
Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

“The exit should be opened by someone close to you” – Effect of weeding – “Stay with Your Community”
2021.09.29
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Message from the new model
2021.09.07
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.

Organization
The Tokyo Foundation for Policy Research
Researcher
Asako Chiba

Progress on MultiLayer-MultiAgent model
2021.08.24
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Akimasa Hirata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata
Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Effect of declining vaccine efficacy
2021.08.03
Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Taisuke Nakata

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Effectiveness of July 12th Emergency Declaration and Accelerated Vaccination Scenario Analysis
2021.07.20
Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Simulation of Medical and Laboratory Resource Optimization Vaccination Effectiveness Study #4
2021.03.30
Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc

Researcher
Tatumi Yamada

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Organization
The University of Tokyo (School of Engineering)
Researcher
Yukio Ohsawa

Simulation of Medical and Laboratory Resource Optimization Vaccination Effectiveness Study #3
2021.03.23
Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Researcher
Setsuya Kurahashi

Simulation of Medical and Laboratory Resource Optimization Vaccination Effectiveness Study #2
2021.03.11
Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc

Researcher
Tatsuo Unemi

Organization
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc.
Researcher
Mitsubishi research Institute, Inc